ERP software and accounting software are two types of business management software tools that are critical for a business to run smoothly. While the two software tools differ in functions and features, they both have a vital role to play in every business regardless of the industry and size. It has long been a myth that only enterprise-level businesses need ERP and accounting solutions. With the complexities involved in running a business successfully, it is imperative that businesses are aware of the software solutions available to them that can help make business management easier. Let’s explore precisely how ERP software and accounting software differ from each other.
Enterprise Resource Planning or ERP software is a software package used to manage the everyday activities of a business in an integrated fashion. ERP enables all the business processes to be connected so they can be managed well, thereby allowing effective business management. For example, an organization has a number of different departments. ERP software helps to connect all these systems, even if they are running on different software and provides key insights to business owners so the business can be run efficiently. ERP is not just a standalone software solution but consists of numerous modules that work together and allow for information to be passed onto a central database from which decisions can be made. A robust ERP solution allows for integrations with a plethora of tools and other software, for this very reason.
Accounting software helps store, report, and analyze business financial data. Whether it is a hundred transactions or thousands of transactions, accounting software makes it easy to record and derive useful information from that data due to its automation capability. It makes accounting faster, easier, and efficient as it eliminates manual errors. As no physical space is required for recording all transactions and financial information, it helps cut business costs, reduces errors, and saves considerable time as all the data is in one place. Accounting software allows quick financial information to be pulled out when needed and enables you to make smart financial decisions through thorough reports.
Best Accounting Software for Businesses | TallyPrime Features |
ERP Software | Accounting Software |
Functionality | |
ERP software is an all-encompassing software package that consists of modules that integrate with the different aspects of a business. Accounting is a part of what ERP offers. ERP includes various other modules such as operations, CRM, procurement, manufacturing, production, and so on. An ERP is generally offered as a customized solution that integrates systems based on the business. | Accounting software is a standalone software package that focuses on just the accounting aspects of a business solely. It has comprehensive features that deal with the financial part of any business only. While it is required to manage the financial part of the business, it does not integrate with the other processes of the business in the way that an ERP usually does. |
Pricing | |
As ERP software is extensive, it costs more when compared to an accounting software package. While this can vary depending on the modules involved and the size of the business, ERP software requires a longer time to be set up. Due to this, it may take longer for employees to understand the true capabilities of the software and how it can benefit them, although today such tools have become easier to comprehend. | Accounting software is provided as a whole package that enables businesses in any industry to manage their accounts and all the nitty-gritty details of their finances. It gives a microscopic view of all the transactions whenever needed and all the details pertaining to those transactions. Accounting software can automate all accounting tasks and is cheaper than an ERP solution. |
Business functions | |
ERP software provides valuable insights into the overall performance of a business rather than a single aspect. For example, ERP software doesn’t only tell you about how efficiently the supply chain operations are taking place. It speaks of where problems occur in the entire business and where processes are taking place smoothly. ERP software is larger in scope and provides an in-depth view. | Accounting software gives detailed information about the financial health of the business. While this is important, it is not as comprehensive as an ERP. Accounting software can help you understand your current business position in terms of profits and losses. It helps you thoroughly understand whether your business is doing well financially or not. |
Utilization | |
ERP software enhances collaboration between employees in various departments because it is used by all the employees to share information across departments. This can help increase transparency across departments and thereby inculcate a culture of trust in the business. The user adoption rate is likely to be higher because everyone is working on the same foundation. | Accounting software helps improve collaboration between people who are in charge of the financial aspect of the business and the stakeholders. Accounting software can help stakeholders get a view of the entire financial health of the business and this can help them make changes that can help cut costs and improve business revenue. |
This depends on your business size, requirements, and your goals. If you are a small or medium-sized business, plugging in accounting software can get you to your business goals. Larger companies, on the other hand, need dedicated ERP systems to manage their business processes. Both software solutions have benefits that can be advantageous to a business in different ways. They both offer automation and allow for real-time reporting so you can do what is best for your business.
Most small businesses tend not to opt for ERP software because they think they won’t utilize the software to its full potential. Contrary to popular belief, ERP software is not an impossible software tool to understand provided you choose the right one according to your needs and what you want to achieve.
TallyPrime offers you the best of both worlds, which is why it is called ERP accounting software.

GST revolutionised the way the country does business. GST being a transaction based consumption tax, it is essential for every business to effectively and accurately compute and record the GST component of their transactions. Effective management of the GST data also makes life easier when it is time to file GST returns. If you find that getting your head around the calculation and filing of GST is just too time consuming, a GST software that is part of a financial and business management software makes work easier. It keeps track of all your financial and GST information in an integrated manner. GST software with financial accounting is a single solution for all your different accounting needs.
A GST software is your one-stop-shop for all your compliance needs. From raising invoices to managing your inward and outward supplies, GST software enables you to keep your books of record up-to-date at all times seamlessly. Tally Prime ensures that your GST returns are in sync with your books of accounts, and reflect the same data as used for filing returns in the GST portal, thus proving to be the right GST return software for you. With TallyPrime you can generate GST reports required for filing with a few clicks. TallyPrime also helps you manage the purchase, inventory and sales aspects of your business. It is a complete business management software with state of the art financial accounting features.
Every country’s government depends on taxes to generate money. This money is used to maintain and develop the country. The government can only run, maintain infrastructure and take care of its people through welfare schemes and incentives when it has enough funds. Hence, it is the duty of every citizen to pay their taxes in order to keep the government functioning for their benefit. Filing your GST returns on time and with complete accuracy is essential for compliance and as your duty to your government.
There are two types of taxes that the government collects; direct and indirect taxes.
As the name indicates this type of tax is levied directly on the income of people and business entities. It is very important to the government as it makes up a large component of the government’s tax revenues. Direct taxes are paid directly by the individual or business to the government. The tax levied is proportional to the income earned by the person or entity.
The lowest income groups are usually exempted from paying tax. This ensures that there is economic and social equality in the collection of taxes from the people.
Indirect taxes are the taxes that the citizens pay when they sell or purchase goods or services.
Indirect forms of taxes are not directly imposed on a taxpayer’s income, but indirectly when they avail or purchase goods and services. It is an easy way to collect taxes from all the people in the country including those who do not pay direct taxes.
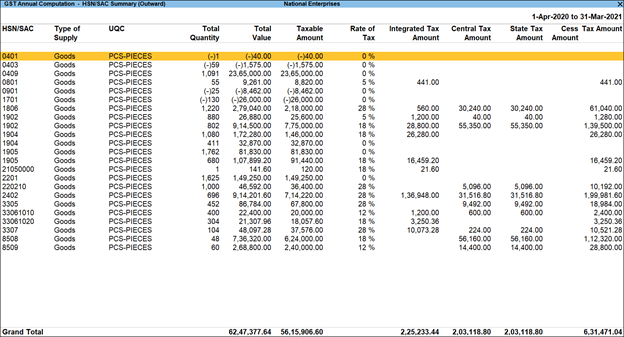
TallyPrime HSN/SAC Summary of Outward Supplies
One of the goals of GST as described above is to digitise the process of taxation to make it easier to do business. When taxes can be filed and paid digitally, it makes good sense to also manage all the financial transactions of businesses digitally. When you use an intelligent business management software that computes GST for every applicable transaction, financial accounting for taxes becomes easier. A GST software also makes the extraction of GST reports and invoices easy and ensures compliance. You can very easily generate the relevant reports and file your taxes on time through the year. Filing your GST returns in a digital format is effortless with GST software.
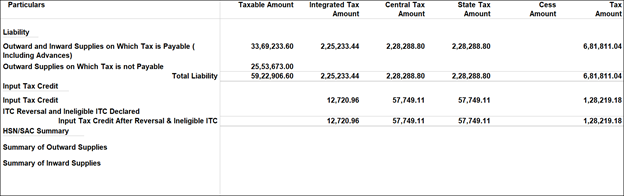
GST Liability, Input Credit, and HSN/SAC Summary In Tally
A good GST software should make every step of managing and filing your taxes effortless. Some of the features to look for in a good GST software are:
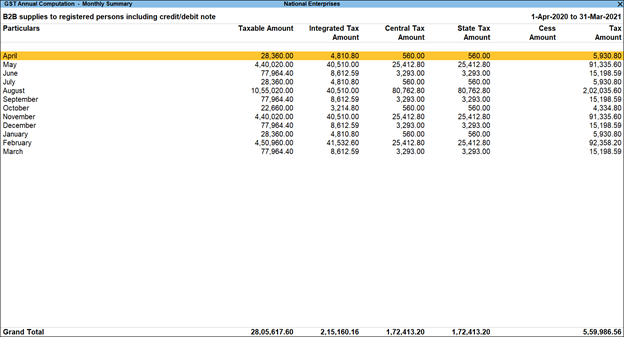
Month-wise Breakup Of GST
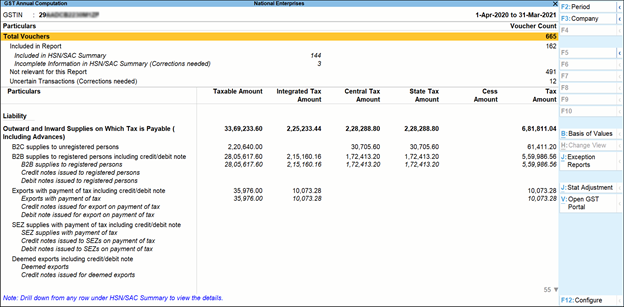
GST Annual Report In TallyPrime
TallyPrime is undoubtedly the bestGST softwarein India because of its extensive features:
So, make your business management digital and enjoy the benefits of accuracy, increased productivity and ease of use with TallyPrime. It gives you a single solution for all your accounting, inventory and sales needs and manages GST seamlessly across all applicable transactions. It keeps your financial accounting and GST details up-to-date in real time. Filing GST details accurately and promptly is simple and straightforward with TallyPrime.
Cloud computing or cloud accounting has become a need of the hour. With remote working taking priority for businesses, there is a requirement to access data across different channels with utmost security and flexibility. Cloud accounting caters to such needs, resulting in scalability and growth of businesses with minimum investment in terms of infrastructure.
The most primary advantage of choosing cloud accounting software is to be able to access business data, remotely. Whatever information is stored in the cloud can be accessed from anywhere in the world and on any device. With so many options available in the market, it could be a daunting task for a business owner to choose the right fit for their business. So how do we find out which cloud-based accounting solution is best for our business?
| Tally Prime on Cloud Service | How to buy and use TallyPrime on a cloud service? |
Here are 5 most important questions that you should ask before you opt for cloud accounting software:
As a small business owner, you may plan to grow your business in the long run. Expanding your operations in terms of adding more people to the team, to increasing more stocks, addition of branches/godowns, etc. would require you to opt for a more flexible option to manage business in a better way. An intelligent cloud accounting software will ensure that it gives you the flexibility to manage your business, just the way you want. Whether it's taking care of your stock levels or accessing your business reports remotely, your cloud accounting software will take care of your current and future business needs with ease.
Any new technology requires a certain kind of training for users. While this could be time-consuming, it is also important that this aspect is not ignored. However, with an easy-to-use software, business owners will feel much more confident in adopting the technology for their needs. A lot of times, organisations feel intimidated with a cloud set up as it involves a complex process of setting up and then training your employees to use the technology. This would be time consuming and could also result in additional expenses as your would need experts to train your employees. A simple one-time set up would mitigate this problem and let you make the most of cloud technology for your business growth.
Small businesses operate within a set budget and so they tend to steer clear of any additional expenses that could be borne by their company. While choosing a cloud accounting software, often business owners get intimidated by the price it comes with. Thus, as a business owner you must always choose the best cloud technology which is also packed with the features that would help you manage your business better. Given the nature of operations of small businesses and the absence of reliable and affordable cloud technologies which ensure a great user experience through high availability and security, it is imperative that business owners use a simple solution offering anytime anywhere access and work collaboratively.
When choosingaccounting softwarefor your business, you obviously look for specific features that would help you manage your finances better, right? Similarly, you should always ask your cloud accounting solution as to which features will you get out of this solution that will be beneficial for your business right now and in the future. From the creation of invoices to tracking expenses to preparingfinancial statementsto stock movements, these are some of the basic features that accounting software usually has. And it is obvious that when you look for cloud accounting software, you expect such functionalities by default. Whether you are traveling or at home, you should be able to access your business reports and get complete visibility of your business data, seamlessly.
Secure data exchange is one of the key things a business owner looks for in accounting software. And with cloud accounting, this activity of working in sync with concerned individuals becomes much easier. With a straight-forward process, the cloud gives business owners an advantage of exchanging data without the need of travelling to another location. A flexible cloud accounting software gives a provision of seamlessly connecting with online and offline users. Let’s say if you have a set of users who are working on a standalone machine /desktop and few users are connected remotely, your cloud accounting software must facilitate all the users to work on the same data without any hindrances. Thus, ensuring greater collaboration and flexibility.
Data security is one of the biggest challenges that companies face, irrespective of the size. While cloud services do promise complete data security, sometimes business owners can’t help but face data leaks and data corruption. Hence, it is crucial that your data is saved on an encrypted disk and securely retained. Automated backups, security controls and user access are the most primary features that would help you safeguard your data with minimum effort.
The goal of a business is to make more money than it spends, which is the profit. However, profit is not the same as profitability, though the two terms are used interchangeably very often. Profit is the amount of money that the company has after paying the expenses. But, profitability in business is the return on investment that the company makes. A profitable company may not be showing profits. This scenario happens when the company reinvests all its money to grow bigger. So, there is no profit left after expenses though the company is showing an excellent return on investment. So, to analyze a company and its performance accurately, one must clearly understand the terms profit and profitability and how they differ.
What is Profti Before Tax (PBT)?-Profit Before Tax Formula with Example |
The company’s financial records will clearly state its income and its expenses of the company. When there is a higher income than expenses, the company makes a profit. This number is calculated on the income statement, and it is a crucial metric to keep track of. So, profit is a precise and directly computed number. Profitability in business is more relative. It is the ability of the company to generate a return on investment with its available resources when compared to another company or project. So, a company that is generating a profit may not be classified as profitable.
So, profit and profitability through similar, must not be confused with each other. The profit tells you how much the company has gained in terms of money after its expenses. Profitability is a measure of the success or failure of the business's ability to make a good return on the money invested in it. It is not a specific amount of cash but uses different profitability ratios.
Profit and profit margins are vital to a business. The profit is the amount of money that is left over from the revenue after the company has paid for its expenses. It is mathematically computed as the difference between the revenue and expenses and is found on the last line of the income statement. Hence it is called the ‘bottom line’. The profit made is essential for the company to keep itself in business and to have enough money to expand and grow without incurring debt. Profit keeps the business solvent. A company's profit can be calculated from the cash flow statement and the income statement. The cash flow statements tells the reader how much money has come in and how much is going out in a particular time period. The difference between the two is the profit or the loss of the company.
Profit can be classified into three categories:
Profitability in business measures how well the company is making returns on the investment of its owners or stakeholders. In a public company, the shareholders observe the profitability of a company to see if they are making a good return on investment (ROI). The profitability measures how well the company is using the resources that are available to it to make money. This includes the assets that it has, such as factories and equipment. The profitability of the company is not the same as the profit. Certain companies reinvest their profits back into the company to expand. So if they are making a profit but are not profitable, they are not serving the purposes of the owners' and shareholders’ investments well. Profitability is very important in companies that are using capital or debt to grow their operations.
We can calculate and measure profitability using profitability ratios such as the return on assets (ROA) or profit margin ratio. This tells us the ratio of the company’s profit compared to the total costs such as equipment, inventory, and supplies. If the ROA is low it means that the company is making too little money compared to what is invested in it. It is not making the owners enough money for their investment, and this may result in fewer investors willing to put their money into the company.
The profit of the company can be the net profit or loss. This is because if there is leftover money after expenses, it is a net profit. But if the expenses are more than the revenues, it is a net loss. The formula for the profit of a business can be calculated from the numbers on the income statement. It is as follows:
Profit = Total Revenue – Total Expenses
This number is calculated and displayed on the bottom line of the income statement. A negative shows that it is making a loss and that corrective measures are called for in order to turn the company around.
We can take the example of a company that generated INR 22,000 in revenue in December and spent INR 12,000 on expenses. The profit would be the difference between INR 22,000 and INR 12,000, which amounts to INR 10,000. This is a positive number which indicates that the company made a net profit of INR 10,000. But, that profit does not indicate that the company itself is profitable. Profitability in business looks at the overall picture of the money that the company is making and compares it to the investment that was made in the company. The most popular profitability ratios that are used for this purpose are:
Profit margin ratio: This is the number that is the most similar to the profit calculation and tells you the difference in the expenses and profits called the profit margin. It is not a number but a percentage. The numbers used to calculate the profit margin ratio are usually found on the company’s income statement. The formula is:
Profit Margin = (Revenue – Expenses) / Revenue
If we use the same example as we did for profit, INR 22,000 is the revenue, and INR 12,000 is the expenses.
So, profit margin = (INR 22,000 – INR 12,000) / (INR 22,000) = 0.45
The profit margin is 0.45 or 45% which means that the company is making 45 paise for every rupee of revenue. A profit margin over 25% is good.
Gross margin ratio: The gross margin ratio compares the gross margin with the net sales. It helps understand how much higher you have priced your products compared to their cost price. So, it is the amount left when you subtract the COGS (Cost Of Goods Sold) from the revenue. The COGS is the amount that is spent to produce the goods sold. The gross margin ratio formula is:
Gross Margin Ratio = (Revenue – Cost of Goods Sold) / Revenue
So if the revenue is INR 22,000 and the cost of goods sold is INR 10,000, we calculate as follows:
Gross Margin Ratio = (INR 22,000 – INR 10,000) / INR 22,000 = 0.54
So the gross margin ratio is 0.33 or 33%. This indicates that the company has 33% of the revue left after spending on expenses.
Return on investment (ROI) ratio: this is the profit of the business compared to the amount of money invested in the business. It tells you your return on investment and is of particular interest to shareholders.
The formula for ROI is:
Return on Investment = (Gain from Investment – Cost of Investment) / Cost of Investment
Let us say that INR 1,000 is spent to market a product that generates INR 1,500 in sales.
ROI= (INR 1,500 – INR 1,000) / INR 1,000 = 0.5
So, the return on the investment of every INR 1 is returning 50 paise. The higher the resulting percentage, the better the profitability of the company.
Profit and profitability are not the same in accounting. A company can generate profit and not be profitable. So, the difference between the two should be well understood. Profit is the amount that the company has left over after paying the expenses. Profitability is how well the company is using the resources that it has in hand to generate revenues. It tells the shareholders how much return the company is giving them for their investment.
The profit a company makes is the difference between the revenue and expenses of the company. A company can make a profit but how profitable it is, depends on comparing its profits to the resources that were used to generate the revenues. The owners and the shareholders of the company put money into the enterprise with the hope that it will give them returns on their money. So the profitability in business gives an indication of whether the company is delivering on this or failing at it.
Investors look for high profitability companies to invest in. This is because these companies are using the money that they have in the form of resources to make the most money. The company that uses its human resources, machinery, and infrastructure to make the most money is a promising investment. When investors compare a highly profitable company to one that is just breaking even, the profitable company is more attractive. Profitability is a reliable measure of a company’s performance regardless of its size and scale.
Profit is the short-term status of the company’s bottom line. It is the short-term income status of the company. Profitability, on the other hand, is a more important long-term metric that is of interest to investors. While the profit calculation gives an indication of the bottom line, the profitability is the measure of the return on investment of the company.
A profitable company is very attractive to investors because the company is making the maximum use of its resources to generate more money. A profitable company will easily attract more new investors to help fund its further expansion and growth. Higher profitability shows the company is more likely to continue keeping the stock and dividend value high. Sustained performance and profitability is more important to investors than profits in the short term.
The ratio of the company’s profits over the investments made in it is the profitability ratio. If the ratio is high, it means that the company is doing well. This ratio can be measured as the net profits divided by the total assets of the company. Most companies that are publicly listed declare their profitability ratios as this is of great interest to the investors. However, other smaller companies must also keep a watch on their profitability ratio.
Generally, a profitability ratio of more than 10% is good because it shows that the company is doing more than merely breaking even. The company is making the best of all the resources at its disposal and building a strong business foundation. Profitable companies usually reinvest their earnings in the company to fuel further expansion and growth.
Lenders and investors alike monitor the profitability of a company to determine if the company will be able to repay its debts. Calculating profitability is important for businesses. But smaller businesses and family-owned businesses may find it difficult to calculate their investments and assets accurately. Tally Prime helps you monitor your company’s performance instantly regardless of the company’s size. Keeping profitability in mind helps long-term planning and reinvestments in the company’s growth.
When a company collects payment in advance for a product or service that has not been delivered, it is called deferred revenue. The treatment of deferred revenue in business accounting is different from a payment that has been made after delivery. This different treatment occurs when the revenue is earned in one accounting period, and its delivery is in a future accounting period. This presents a unique situation in which the accountant will have to treat the revenue differently when preparing the business financial reports and statements.
Deferred revenue is also called unearned revenue because it is a revenue payment that is received before the company has earned it by delivering the product or service. This presents a unique situation when the company uses accrual accounting. Accural Accounting requires that the revenue and matching expenses should be accounted for in the same accounting period. But when a company receives an advance in one accounting period and then delivers the goods or service in the next, there is no match of the revenue and expenses. When you receive a retainer or a booking amount for a service or product, this situation arises.
Accrual accounting recognizes a payment receipt as revenue only when earned. In reality, customers often make advance payments towards goods and services that have to be recorded in the books of accounts. So, instead of recording this deferred revenue as sales revenue, it is listed on the balance sheet as a liability and not recorded in the income statement.
Since the deferred revenue payment is received for a service or product that is yet to be delivered, it is a payment for something owed to the buyer or customer. This makes it a liability rather than revenue. As the product or service is delivered in portions or completely, the appropriate amount of deferred revenue is recognized on the company’s income statement. This is in line with the GAAP guidelines for accounting conservatism.
The balance sheet records the deferred revenue amount as a short-term or current liability as the service or product that is paid for is expected to be delivered in the short term. So, it is a debt that is owed to the customer or buyer. If the service or the product is not delivered, the money may be liable to be returned. The collection of the amount also means that the company owes the service or product to the buyer.
There is a difference between the deferred revenue and accrued expenses. They are both listed as a liability on the balance sheet. But deferred revenue is money received in advance for services/products not yet delivered, and accrued expenses are amounts for which the company has received services/products and has not paid for as yet.
An example of this could be a performance bonus that an employee who performs well earned every month. The amount is calculated and adds up but is only paid at the end of the defined period. Since the amount owed increases over time, it is an accrued expense and not a deferred revenue.
Deferred revenue is categorized as a liability on company balance sheets. This is because the company has received the deferred revenue amounts as an advance. The company is then liable or obliged to deliver the service or product that the advance was paid for. If the company is unable to deliver the service or product, it may be liable to repay the amount that was collected as an advance unless there are other terms and conditions agreed upon in the contract between the buyer and seller.
Deferred revenue is unique to accrual accounting systems where there must be a matching of the expenses and revenues that relate to each other. However, if a business uses cash basis accounting, there is no worry about deferred accounting. The money you receive is recorded as soon as you receive it, and there is no need for any other adjustment or matching principle. You record the transaction exactly when it happens.
In accrual accounting, the receipt of payment can only be recognized as a revenue payment when the company has earned it. So, when an advance payment has been received, it is recorded as deferred revenue. When the company performs the actions that earn that revenue, it gets recorded as revenue, and this is called revenue recognition. The principle that states when money can be recorded as revenue is called the revenue recognition principle. The revenue recognition principles that are defined by Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) for different business types and industries are the most commonly followed principles.
The principle of deferred revenue may be confusing to some as it uses the word ‘revenue’ but is classified as a liability. This is because the money has not been earned yet. It is an amount that is liable to be returned in case the company is not able to deliver the product or service. Some industries have very strict methods and principles by which they put aside the deferred revenue until it is earned.
The principle of deferred revenue is useful to prevent overvaluation of the business by including payments for deliverables that haven't been delivered yet. For example, a yearly subscription service may collect the entire yearly subscription upfront, but the services will be delivered over the next year. By using the deferred revenue system, the company’s accounts present a realistic picture of what it is actually worth and how it is performing through the year. It is also good accounting practice to be very discerning about the amounts that are classified as assets and liabilities on the financial records. Following the accounting principles ensures that liabilities such as the deferred liabilities are not misclassified as cash.
Deferred revenue is easier to understand with an example that shows each step and entry that is made.
A company agrees with a client to deliver a service for the next 12-months and collects the entire annual fee of $1200 upfront. So the company records a revenue of $0 for the month but creates an entry for the liability in the deferred revenue account amounting to $1200. The cash amount on the balance sheet increases by $1200.
Account | Debit | Credit |
Cash | $1200 | - |
Deferred Revenue(Liability) | - | $1200 |
After every month, the company records a revenue of $100, and the deferred revenue account gets reduced by $100. This recording of revenue and reduction of the deferred revenue continues for 12-months.
Account | Debit | Credit |
Deferred Revenue(Liability) | $100 | - |
Revenue | - | $100 |
At the end of the 12-month agreement period, the earnings or revenue of the company would have shown the entire $1200, and the deferred revenue from that particular transaction will be $0.
By the principles of accrual accounting, it is necessary to record deferred revenue when money is collected in advance of the product or service being delivered. It is recorded as a liability until the product or service has been delivered. If the product or service is delivered in installments, the proportional installment of the money recorded as deferred revenue is transferred to the company’s revenue account.
Cash basis accounting does not follow this principle and records the money as it is received. This is easier to maintain when customers are very volatile and changeable in their payments. However, it can artificially inflate the company’s value by showing such advance payments and subscriptions as revenue when they are yet to be earned.
The deferred revenue principle also affects the cash flow statement. This statement would record the payment in the example above as cash from operating activities on the date when it was received. No adjustment entry is made in the cash flow statement.
We often look at the financial accounting reports of companies and businesses. These reports are prepared for a specific period. The time period assumption or periodicity assumption is important in financial accounting and reporting. When you read an accounting report, ensure that you have familiarized yourself with the time period it is prepared for. The time period or accounting period concept may vary from country to country. While specific reports are calculated for a period called the fiscal year, others are prepared on a monthly, quarterly, or half-yearly basis.
Accounting Cycle Definition and steps in Accounting Cycle process | Best Practices to Evaluate, Purchase and Implement Business Accounting Software |
The life of a business can and should be divided into equal time periods. The financial reports are prepared for time period assumption, periodicity assumption, or accounting time period. The length of the time period depends on the report and what it is needed for. Generally, an accounting period is a quarter, six months, or a year. The meaning of the report should be inferred depending on the accounting period it is made for.
It is essential to divide the reporting time into equal periods. This helps in evaluating the performance over a period of time and compare it to equal periods of time. Self-evaluation is essential to understand where there is room for improvement. Evaluating the finances of a company over fixed sections of time helps in making decisions based on its financial performance.
The most commonly generated statements for a time period are the income statement and the balance sheet. The income statement indicates how profitably the company has operated, and the balance sheet gives an overall picture at the end of the financial period. The statement of cash flows gives the details of cash inflow and outflow in the accounting period. The statement of retained earnings details the distribution of the earnings among the debt repayment, business growth investment, and the business owner’s accounts.
These reports are essential to understand the company's finances. In addition to business managers,financial statements are also of interest to investors, creditors, and government agencies to whom they are submitted. Most people evaluating a company will do so by studying the financial statements over a few accounting periods.
The period assumption is the division of time into equal sections for financial reporting. The financial reportsfor specific accounting periods help study the business report trends over successive time periods. For internal purposes, financial reports may be prepared every month. Some companies create statements every four weeks instead of every month. This would create 13 accounting periods in a month.
The primary time periods for the year are the fiscal year which is not always the same as a calendar year. While some companies may use the calendar year for internal purposes, the fiscal year generally starts on the 1st of April. So an annual report would usually span the period of 1st April of a year to the 31st March of the subsequent year. A monthly report would usually be for the calendar month. You can compare the business reports of two equal sections of time to compare the company's performance in other financial aspects.
Another importance of the period assumption is the accounting matching principle. By this principle, the related revenue and expense should be recorded in the same time period. So for every debit, the matching debit should be recorded in the same accounting time period. So, the accounting time period should be defined clearly to adhere to this principle.
The going concern principle assumes that the company will continue to operate without liquidation. By this principle, the accrued expenses for a time period is carried forward to the next. This can only be followed when there is a clearly defined accounting period concept.
Financial accounting starts with the simple recording of a transaction and then moves to the consolidation of the entire company's financial information for a financial period. The step-by-step process of doing so is called the accounting cycle, and it starts with a transaction and ends with detailed financial reports. An accounting cycle should be strictly followed to ensure proper accounting for and reporting in each accounting period.
The ten steps that comprise the accounting cycle are:
Registration





